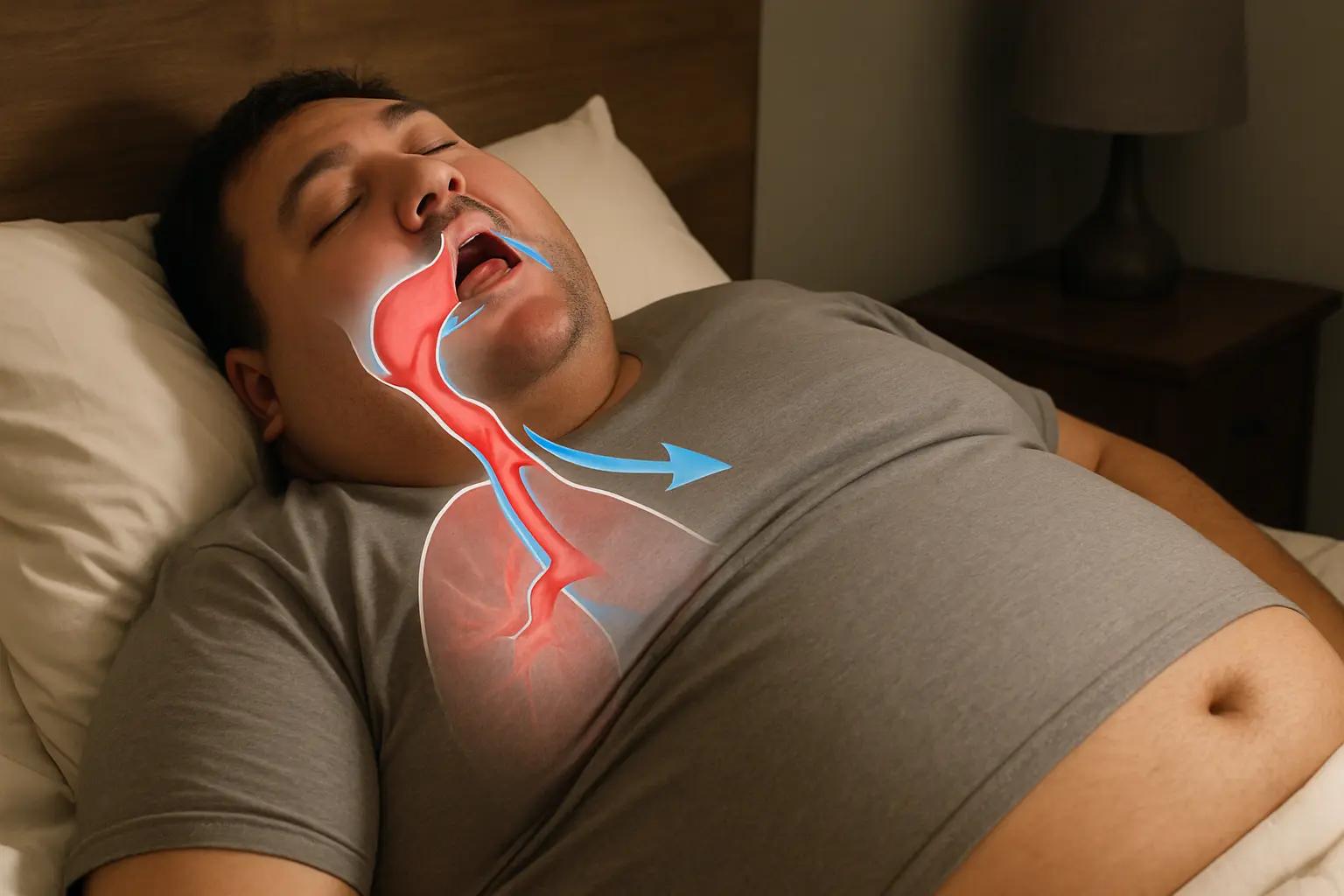
The Role of Weight and Obesity in Snoring and Sleep Apnea
Weight plays a significant role in airway stability during sleep.
Excess fat around the neck and torso can narrow airways, increase snoring intensity, and contribute to obstructive sleep apnea (OSA).
How Weight Affects Snoring
- Neck circumference: Thicker necks reduce airway diameter
- Fat distribution: Central obesity can impact chest wall mechanics
- Muscle tone: Excess weight may reduce airway support muscles
- Inflammation: Obesity is associated with systemic inflammation, worsening airway sensitivity
SnailSleep monitoring shows users with BMI >30 have 45% higher snoring intensity than those with BMI <25.
Data Snapshot: BMI vs. Snoring and OSA
| BMI Category | Avg. Snore Score (0-100) | % with Mild OSA | % with Moderate/Severe OSA |
|---|---|---|---|
| Normal (18.5–24.9) | 47 | 12% | 3% |
| Overweight (25–29.9) | 58 | 25% | 10% |
| Obese (30–34.9) | 67 | 35% | 18% |
| Severe Obese (>35) | 74 | 42% | 27% |
Even moderate weight gain can significantly increase snoring and apnea severity.
Physiological Mechanisms
- Airway narrowing → tongue and soft palate collapse during sleep
- Chest wall restriction → reduced lung volume, worsening airway obstruction
- Inflammatory response → edema in upper airway tissues
- Hormonal changes → leptin resistance and impaired respiratory drive
Strategies to Reduce Weight-Related Snoring
- Weight loss interventions — diet, exercise, or medically supervised programs
- Positional therapy — side sleeping to reduce airway collapse
- CPAP or oral devices — if moderate/severe OSA is present
- Strengthen airway muscles — myofunctional therapy for tongue and palate
- Monitor changes — SnailSleep tracks snoring intensity relative to weight loss
Real-Life Case: Marcus' Weight Loss Journey
Marcus, 39, with a BMI of 32, experienced loud snoring and daytime sleepiness.
After a 12-week weight loss program, his BMI dropped to 28.
SnailSleep tracked a snoring intensity reduction from 71 to 50, and Marcus reported improved energy and better overall sleep quality.
Related Articles
- Sleep Apnea and Weight Management: A Critical Link to Better Sleep and Health
- When Snoring Gets Dangerous: Early Warning Signs of Sleep Apnea
- How Alcohol and Late-Night Eating Affect Sleep Quality and Snoring